Understanding Structured vs. Unstructured Data: Why It Matters and How Hunni Helps
Data is the lifeblood of modern businesses. From customer information and financial records to social media interactions and email correspondence, organizations generate and rely on vast amounts of data daily. However, not all data is created equal. It falls into two main categories: structured and unstructured data. Understanding the difference between these data types and knowing how to manage them efficiently is critical for business success.
What is Structured Data?
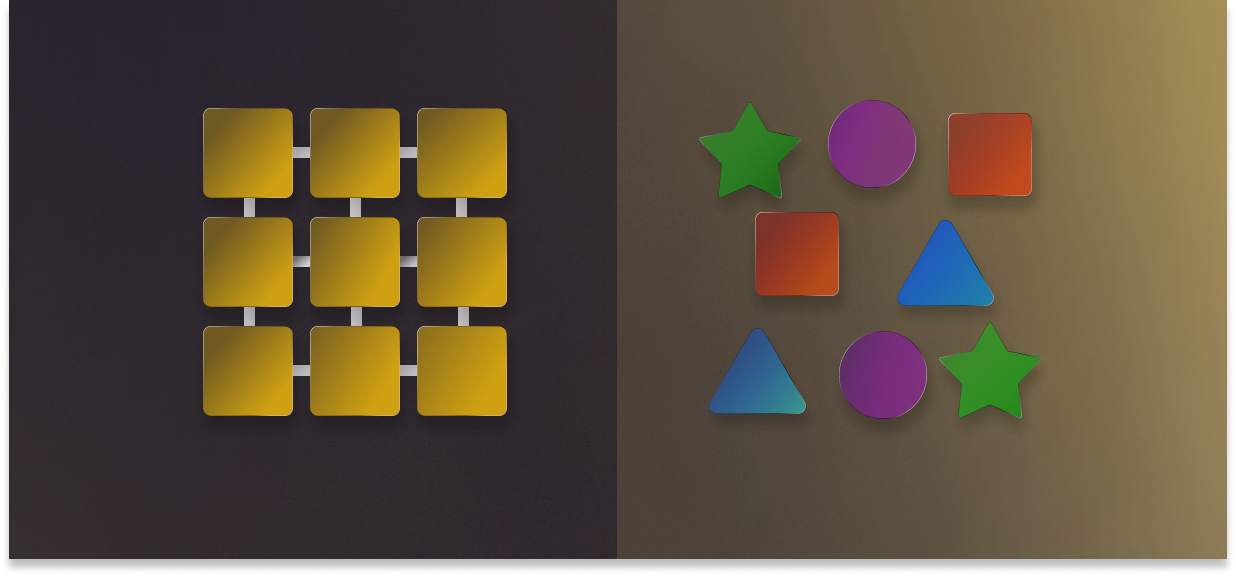
Structured data is highly organized and formatted in a way that makes it easily searchable and processable by traditional databases. It typically resides in relational databases and is stored in tabular form with rows and columns. Examples of structured data include:
- Customer records in a CRM system
- Financial transactions in an accounting database
- Inventory data in an ERP system
Because structured data follows a predefined schema, it is straightforward to analyze and integrate into business processes, enabling organizations to generate reports, track performance metrics, and make data-driven decisions with confidence.
What is Unstructured Data?
Unstructured data, on the other hand, does not have a predefined format, making it more difficult to store, process, and analyze. It includes data types such as:
- Emails and text documents
- Images, videos, and audio files
- Social media posts and chat messages
- PDFs, spreadsheets, and presentations stored across multiple platforms
Unstructured data accounts for nearly 80% of enterprise data, yet businesses often struggle to extract meaningful insights from it because traditional database systems cannot efficiently manage it.
The Risks of Unstructured Data Silos
When unstructured data is scattered across different systems, personal devices, or unknown locations, it creates significant risks, including:
- Inefficiencies – Employees spend valuable time searching for data instead of leveraging it.
- Data Staleness – Outdated information leads to poor decision-making.
- Errors and Inconsistencies – Manually tracked data increases the likelihood of inaccuracies.
- Security Risks – Sensitive information stored in unmonitored locations may lead to compliance violations or data breaches.
Without a reliable way to convert unstructured data into structured, actionable insights, organizations miss out on opportunities to optimize operations, enhance customer experiences, and improve overall business intelligence.
How Hunni Transforms Unstructured Data into Business Value
Hunni bridges the gap between unstructured and structured data, empowering non-technical users to easily turn unstructured data into structured data efficiently and distribute it to whomever needs it. Giving teams easy access to dynamic structured data through Hunni, reduces the risks, improves efficiency, enhances collaboration, and enables easier integration into other tools.
By leveraging Hunni, businesses can harness the full potential of their data, eliminating inefficiencies and unlocking new insights that drive growth.
Conclusion
Structured and unstructured data play essential roles in modern business, but failing to manage unstructured data effectively can lead to inefficiencies, errors, and security risks. Hunni provides the tools needed to transform scattered, unstructured data into structured, usable information, without requiring technical expertise.
Discover how Hunni can help you streamline your processes and unlock valuable business insights today.